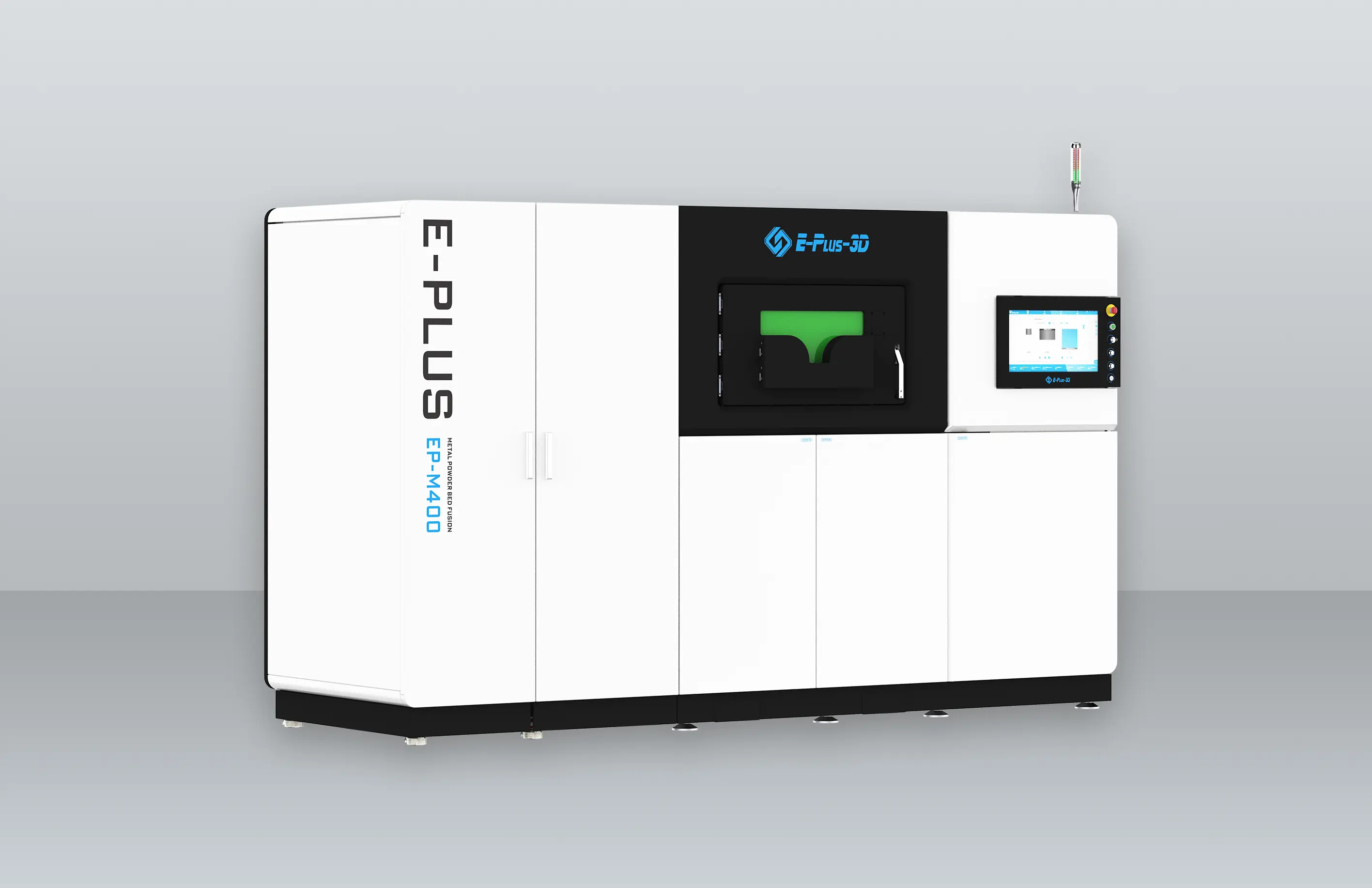
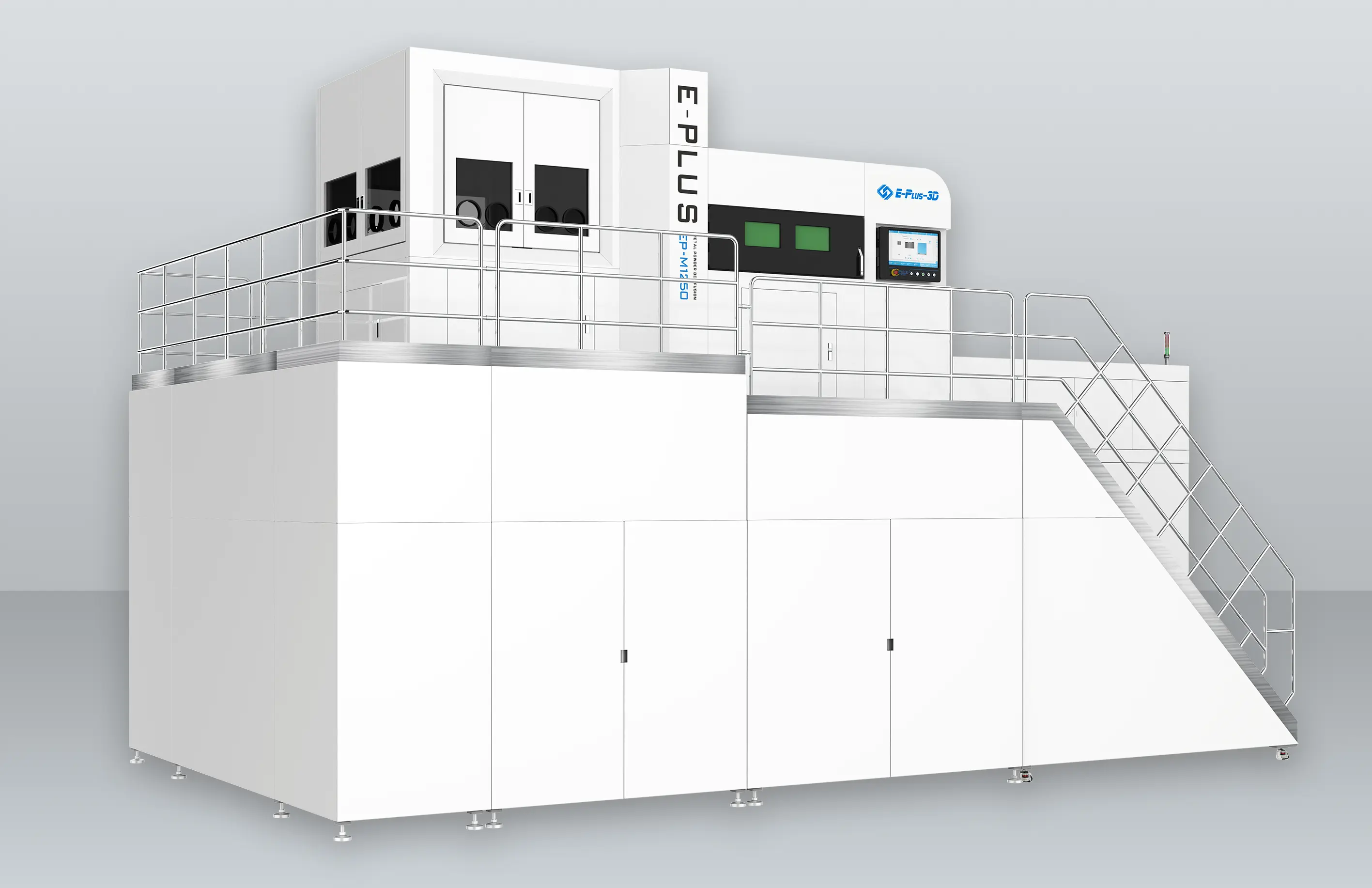
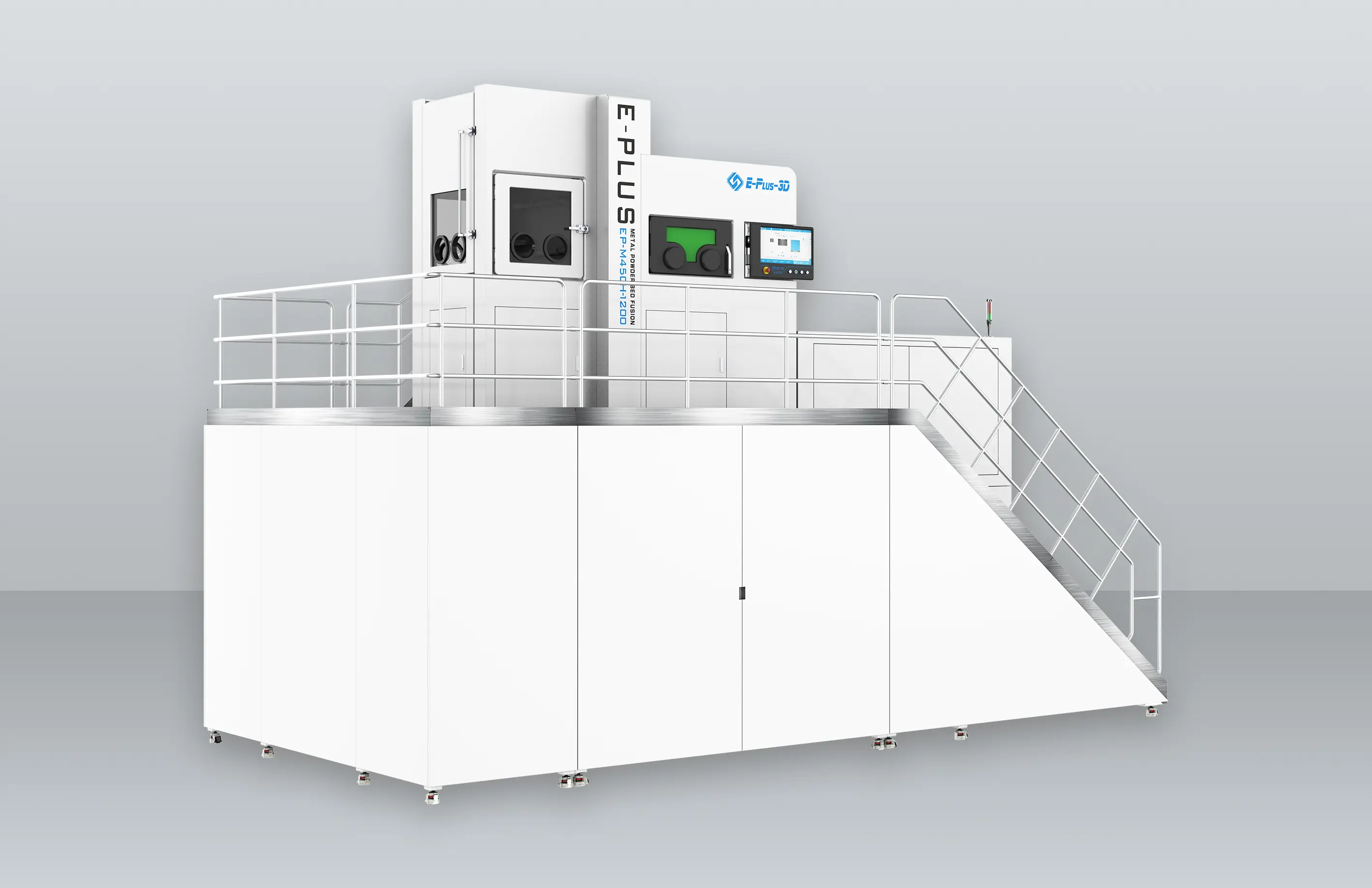
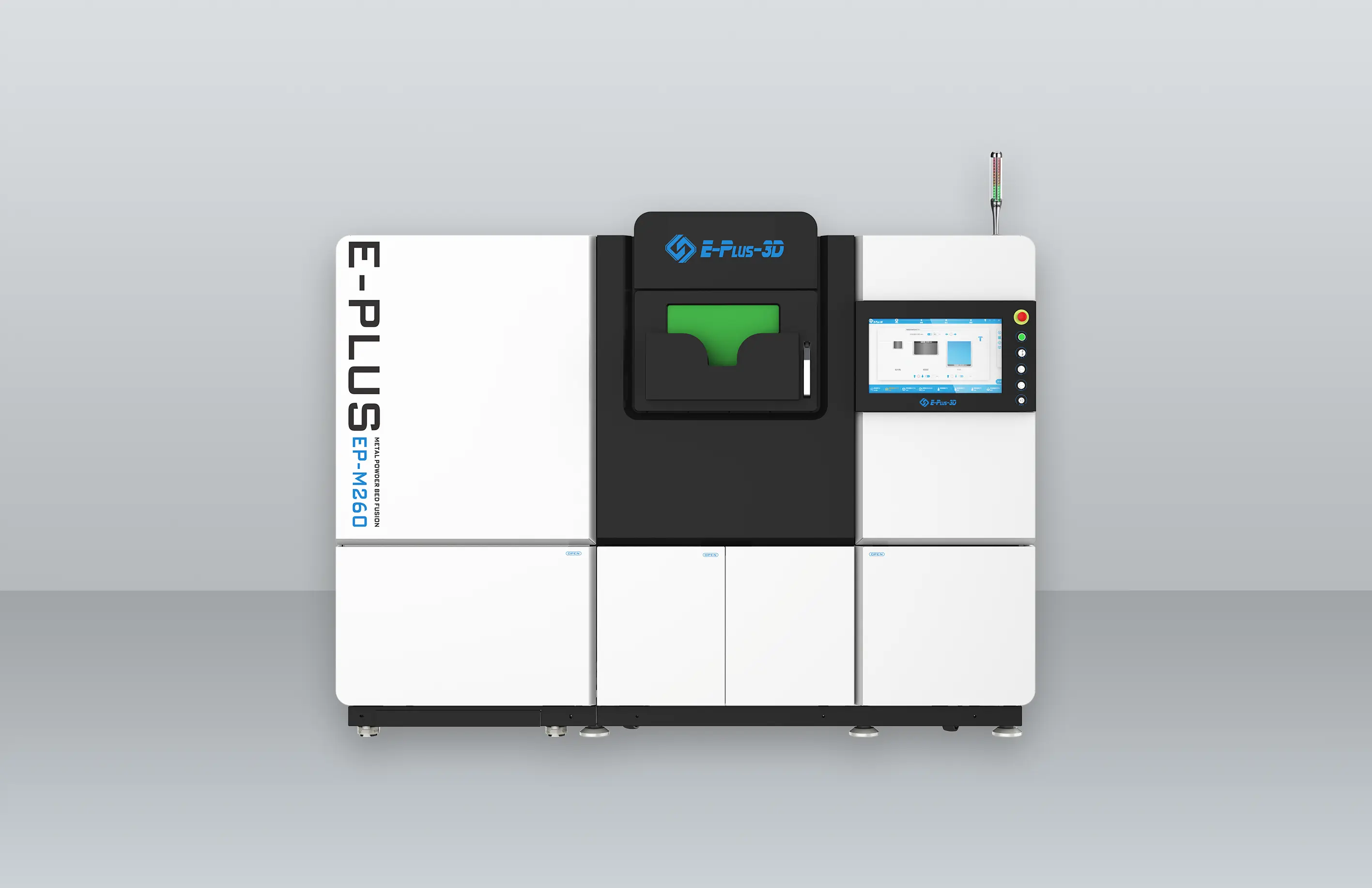
3D printing materials are as important to 3D printing as water is to fish. One of the keys to advancing professional 3D printing applications, especially when it comes to end-level applications of this technology, is the development of material-based solutions.
The development of 3D printable materials in the past has resulted in more and more materials being incorporated into 3D printing applications in different industries. Due to innovations in materials such as titanium alloys, nickel alloys, carbon and glass-filled nylon powders and resins, the application base of related 3D printing technologies has expanded rapidly.
Therefore, there are several major development trends for 3D printing materials in the future. The most interesting of these trends - high viscosity ceramic pastes can be used in photopolymerization technology. In the current search for a viable ceramic 3D printing solution, researchers are improving ceramic powders for use in barrel photopolymerization systems and adding ceramic powders to photocurable resins to claim fully dense ceramic parts.
Another trend in 3D printing materials involves the manufacture of metallic platinum formulations used in powder bed fusion processes. Due to its excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and high temperature resistance, platinum metal is at the forefront of precious metal-based 3D printing technology, which has good application prospects in aerospace and medical applications.
The last major trend in 3D printing materials is the development of carbon-reinforced polymers used in selective laser sintering (SLS) technology for aerospace applications. Similar graphite-reinforced polymer products are being used in automotive applications.