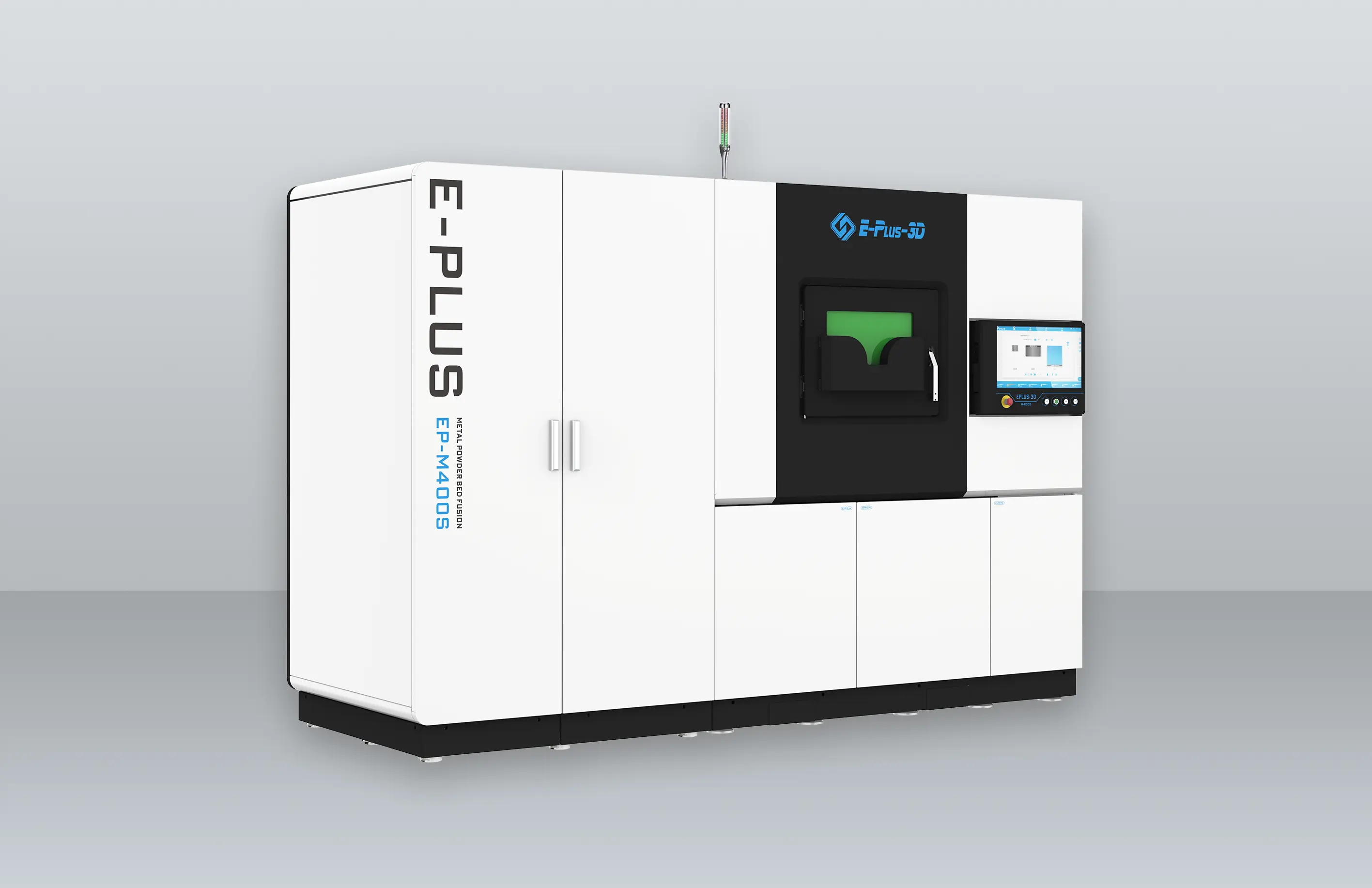
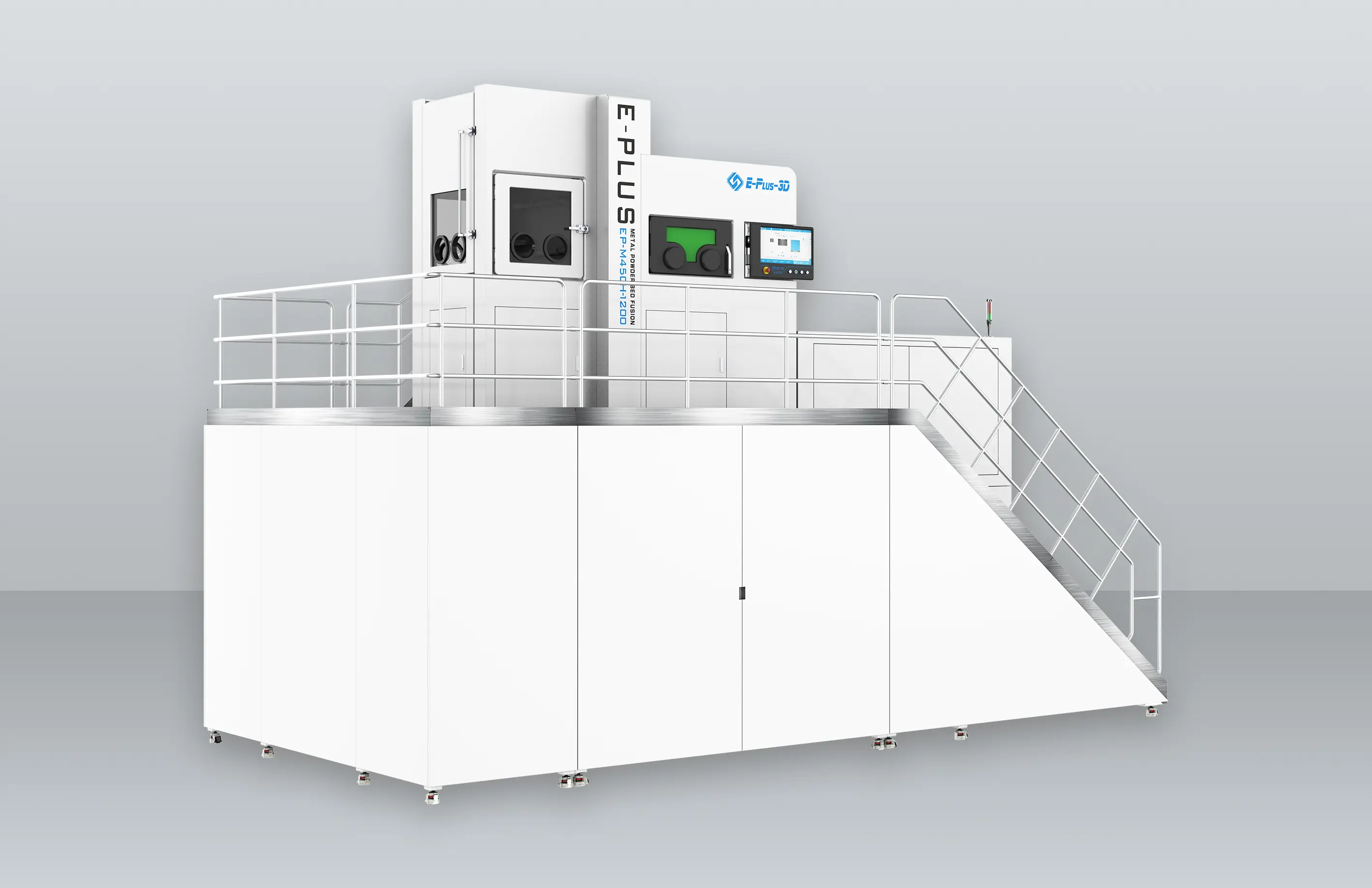
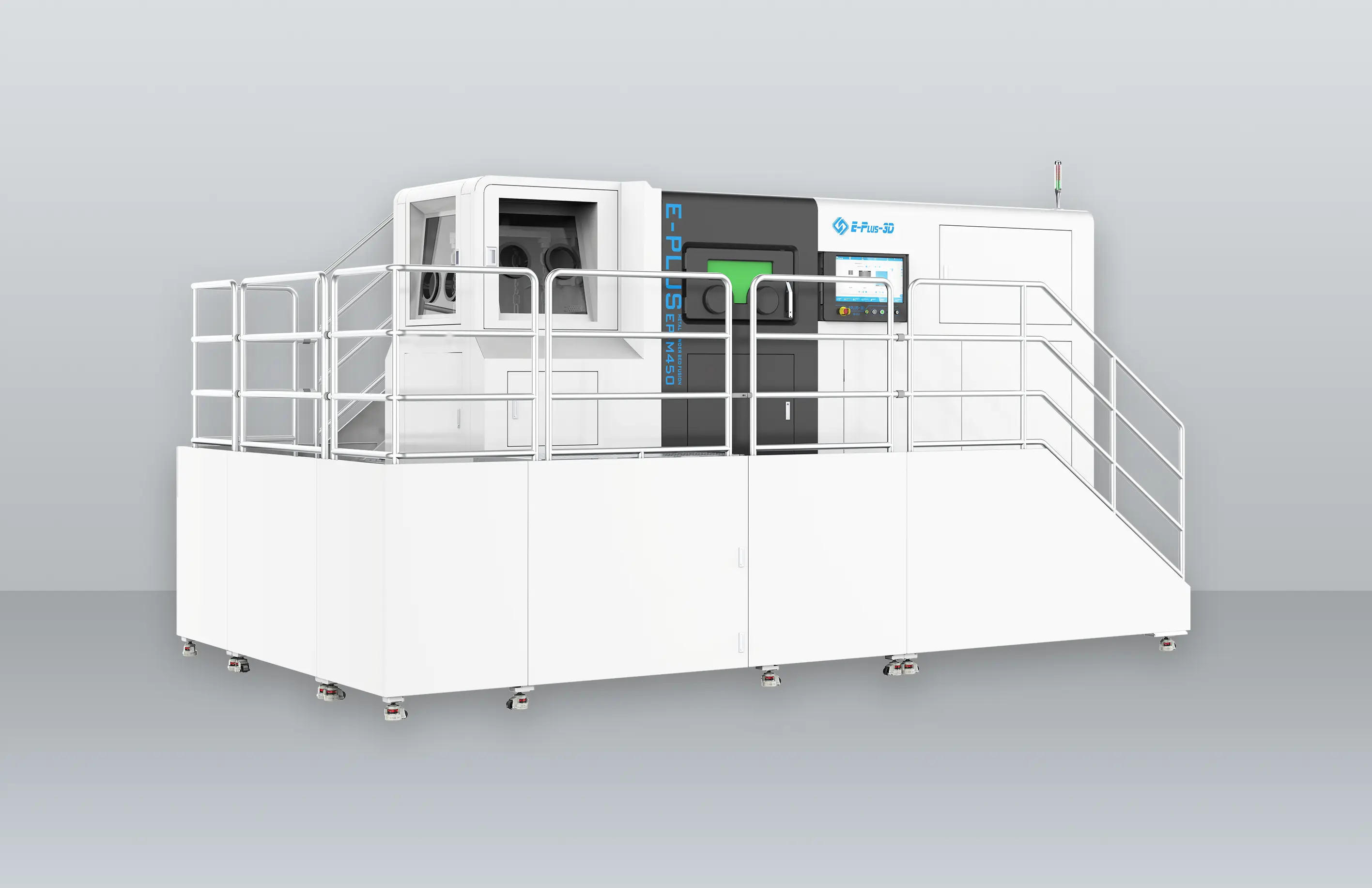
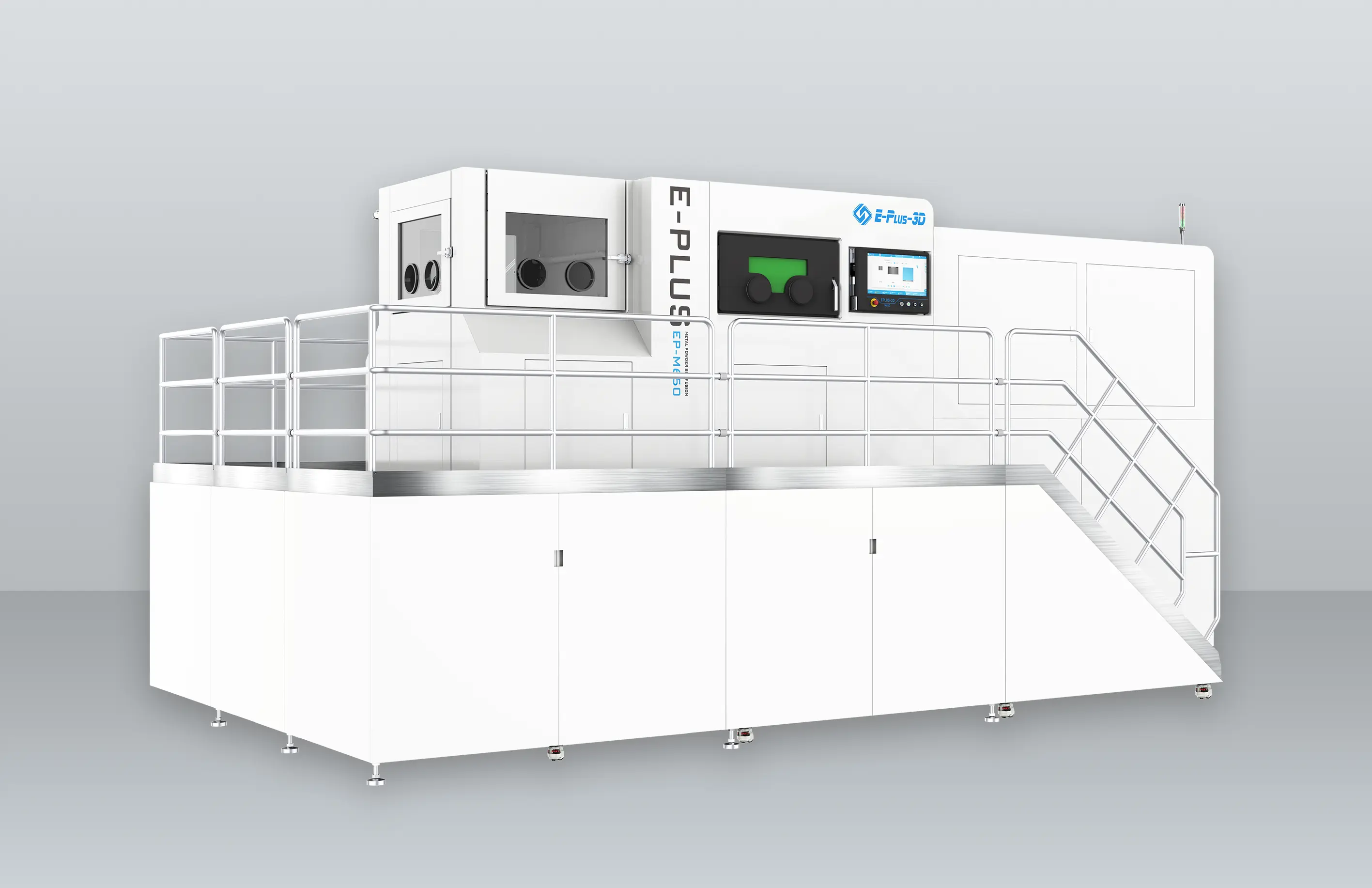
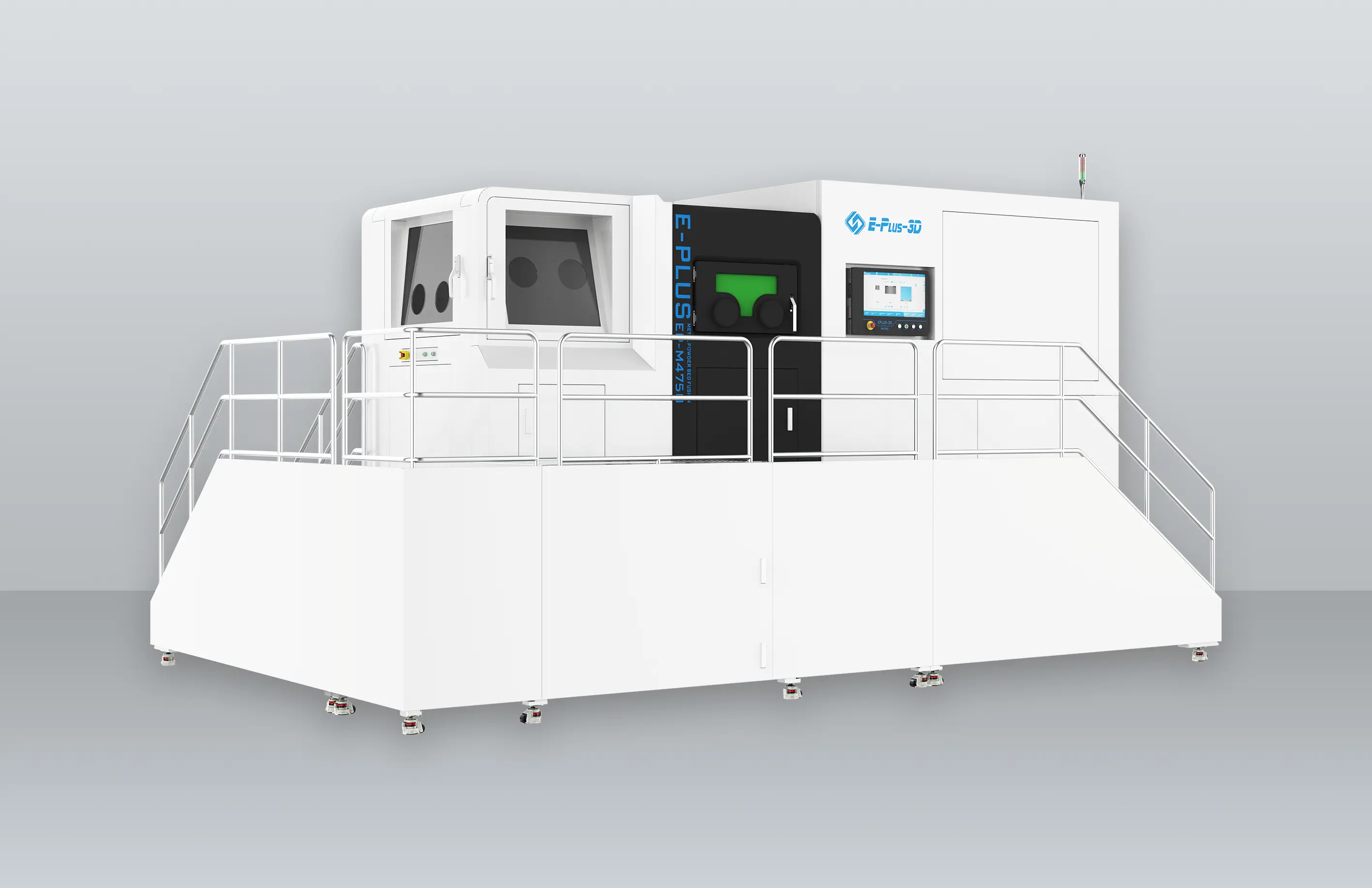
Turbine blades are one of the most important components of an engine, and the materials used are usually very expensive. The turbine blade is thin and easy to deform during processing, and the processing material Monel alloy, Inconel, titanium and nickel based alloy increases the difficulty of processing, which puts forward higher requirements on the processing technology and the tool used for processing. In this issue, we show the CNC machining, 3D printing and casting process of turbine blades.
CNC
CNC technology of blade, including clamping method, programming, cutting technology, c, online detection, etc. The material waste of CNC machining technology is very serious.

3D Printing
The manufacturing advantages of 3D printing are not only reflected in saving materials and reducing costs, but also in greatly shortening the manufacturing time of blades. A new type of gas turbine blade produced by Siemens engineers using additive manufacturing technology can shorten the whole cycle from design to production from two years to two months, greatly improving production efficiency.

Blade ceramic core

Wax mold

Turbine blade after post-treatment
The surface of the blade casting has no metallic luster. After the subsequent machining, drilling, polishing and grinding, it is the state we usually see. This process is also essential for 3D-printed blades.